CNC lathes find widespread applications in various industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, and healthcare. However, individuals unfamiliar with this technology might have some confusion about what CNC lathes are, how they operate, and their specific applications. As a professional company specializing in manufacturing, production, sales, and services, HAISHU aims to provide a detailed explanation in this article about CNC lathe, including their working principles, key components, and application examples. If you have any further inquiries or would like to gain more knowledge about CNC lathe, please feel free to contact us via phone or email.
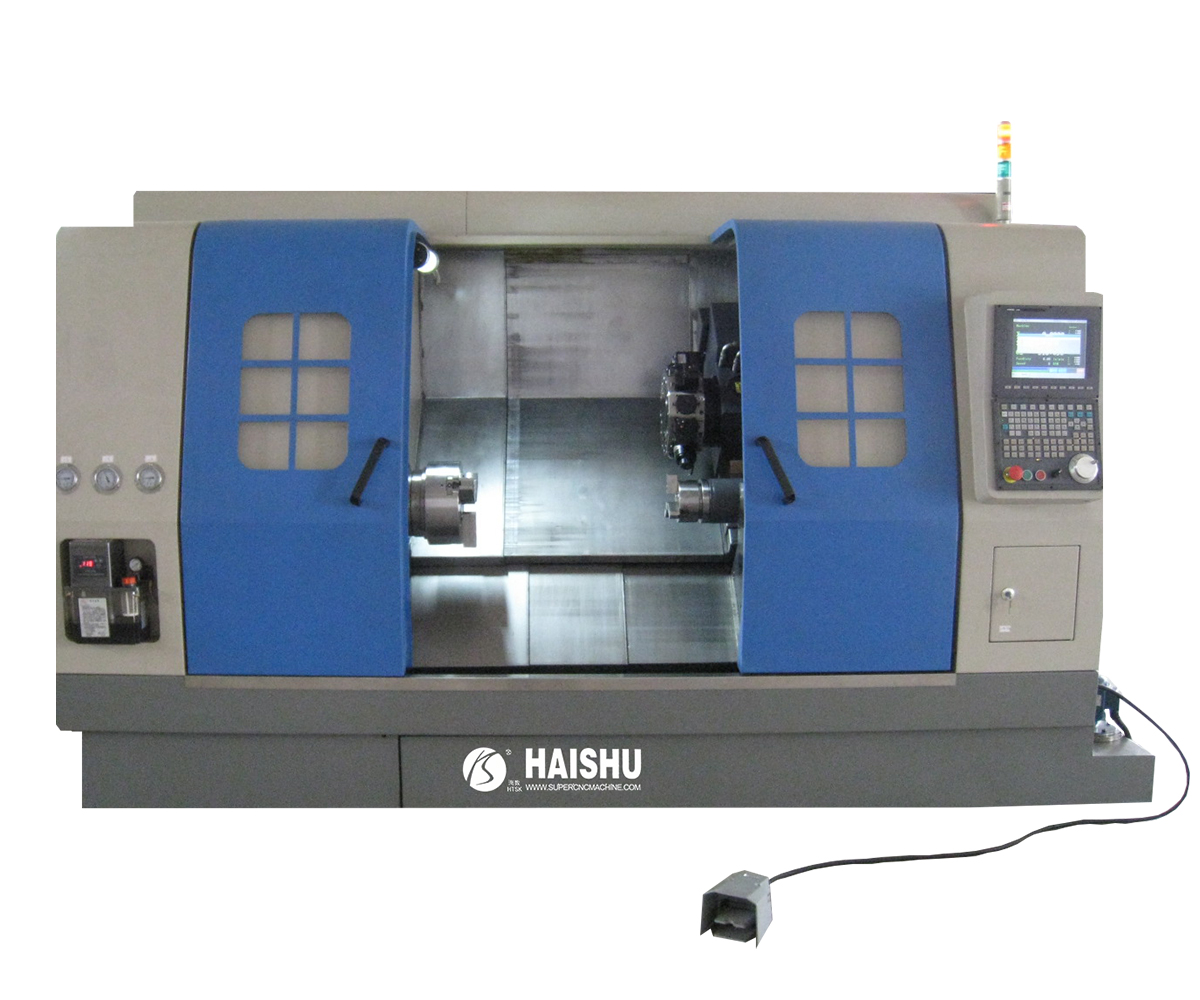
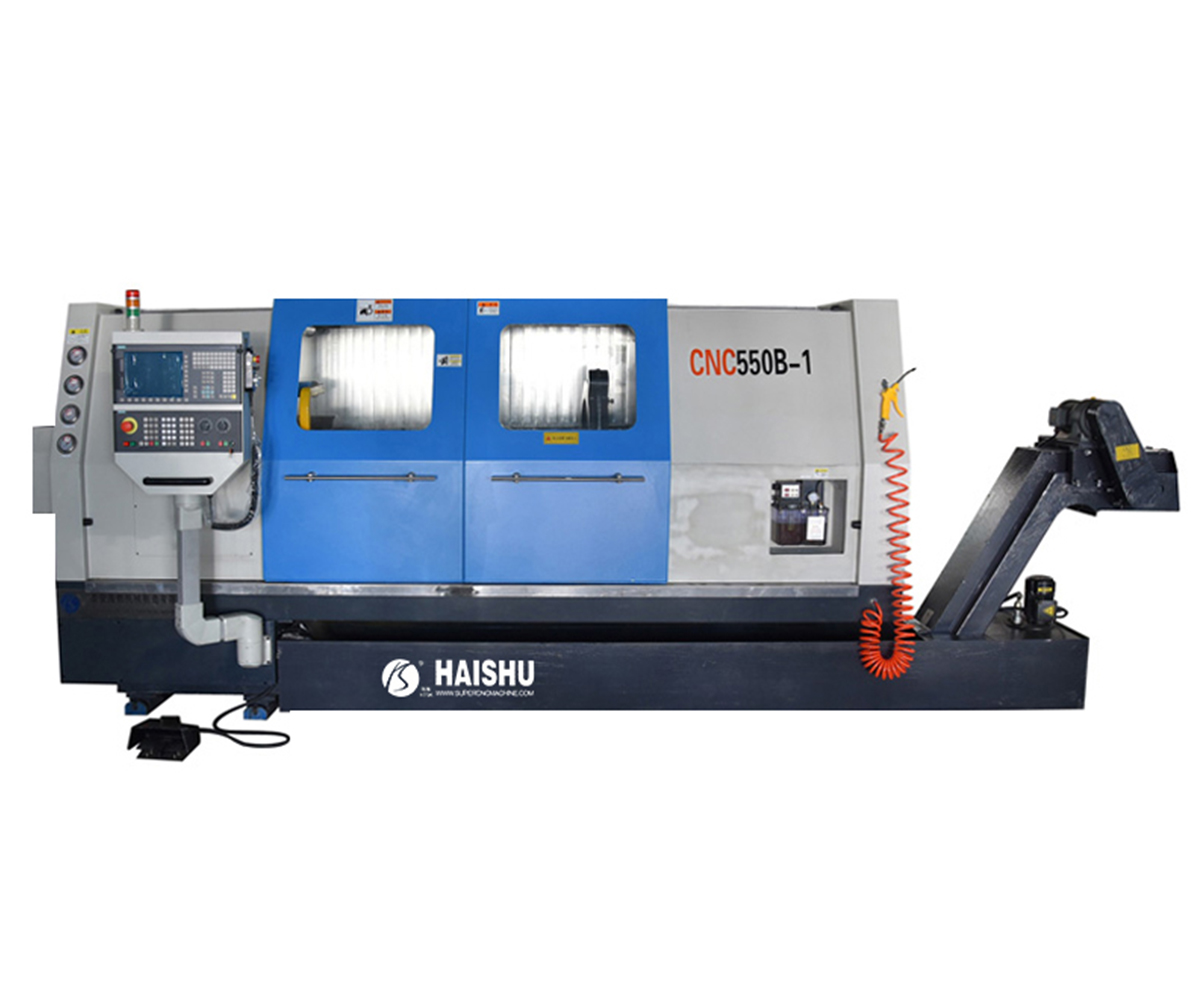
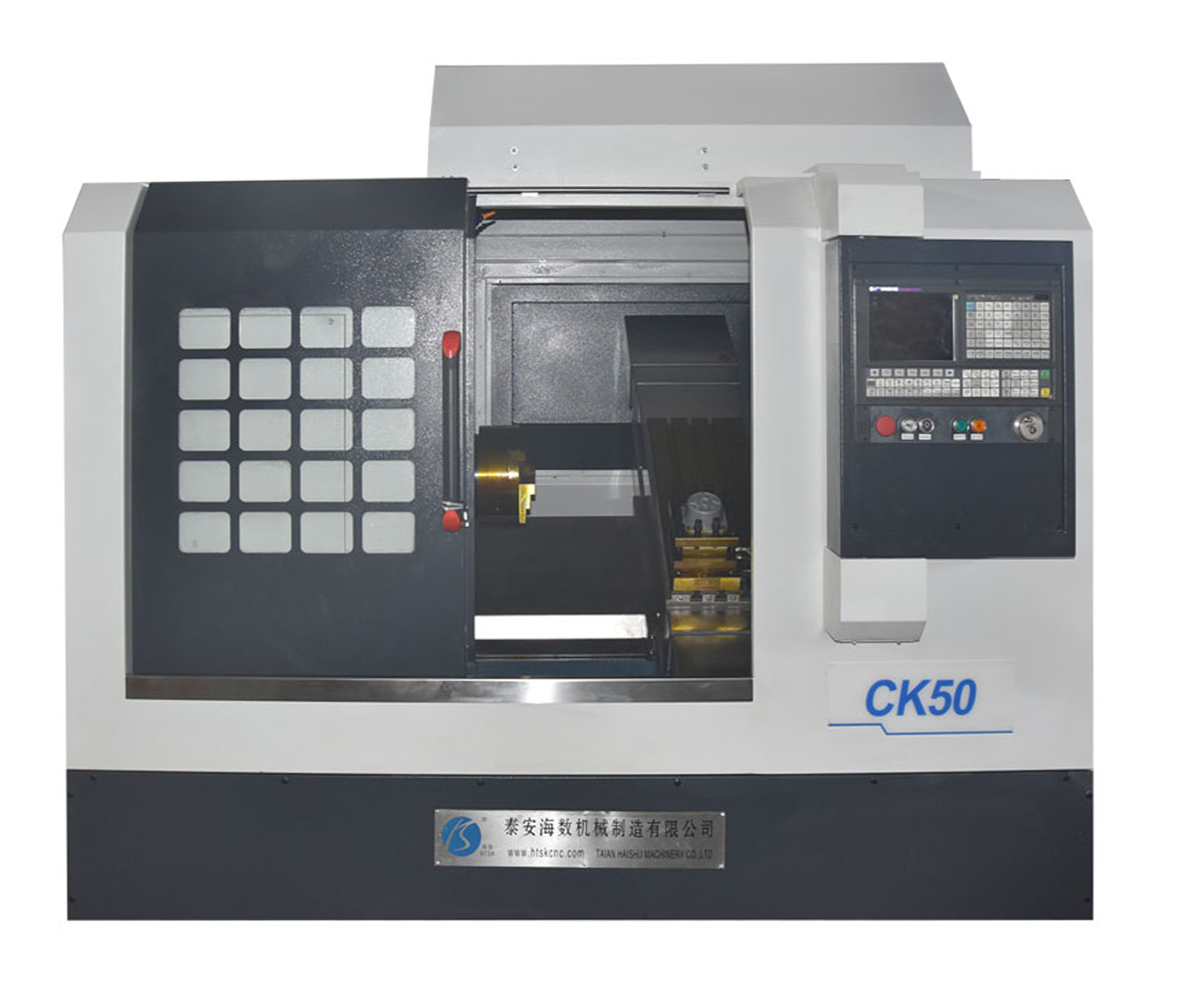




1. What is a CNC Lathe?
1.1 Definition and Overview of CNC lathe
A CNC lathe (Computer Numerical Control Lathe) is an advanced machine tool that utilizes computer numerical control technology for automated machining operations. Compared to conventional lathes, CNC lathes offer higher precision, improved production efficiency, and greater flexibility.
1.2 What is Difference between CNC lathes and Conventional Lathes
CNC lathe enable automated control through computer numerical control technology, providing high precision, repeatability, and machining flexibility. In contrast, conventional lathes rely on manual operation, with machining precision and efficiency limited by the skills and experience of the operator. CNC lathe offer higher production efficiency, reduce the need for manual intervention, and allow for quick adjustments of tool paths and machining parameters.
HAISHU specializes in the production of CNC lathe. With the advancement of technology and the evolving times, CNC lathes are gradually replacing conventional lathes, becoming the primary tool for mechanical machining. Therefore, our company’s main focus and development direction are centered around CNC lathe.
2. Working Principles of CNC Lathes
2.1 Basic Principles of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) Technology
The CNC machining process involves designing the workpiece, developing machining strategies, writing machining programs, transferring programs to the CNC system, parsing and executing programs, machining the workpiece, and monitoring and adjusting the process. Firstly, a three-dimensional model of the workpiece is created using CAD software. Then, machining strategies are formulated to determine cutting paths and parameters. Next, machining programs are written using CAM software to translate the strategies into machine instructions. After transferring the program to the CNC system, the controller parses the instructions and controls the motion of the spindle, tool, and workpiece. Following the program instructions, the tool performs cutting operations on the workpiece, while the controller monitors the process in real-time and adjusts parameters to enhance machining quality.
2.2 Control System and Programming of CNC lathe
The control system of a CNC lathe consists of a controller, drivers, a programming interface, and program memory, among others. The controller receives and interprets the machining program instructions, while the drivers convert control signals into voltage or current signals to drive the motors for motion. The programming interface facilitates interaction between the operator and the system, and the program memory stores machining programs and related data. The programming process involves utilizing G-codes and M-codes to control motion and auxiliary functions, establishing coordinate systems to determine positions, and defining tool paths for machining operations. HAISHU offers CNC system assembly based on customer requirements, allowing customers to choose their preferred systems or configurations for the machine.
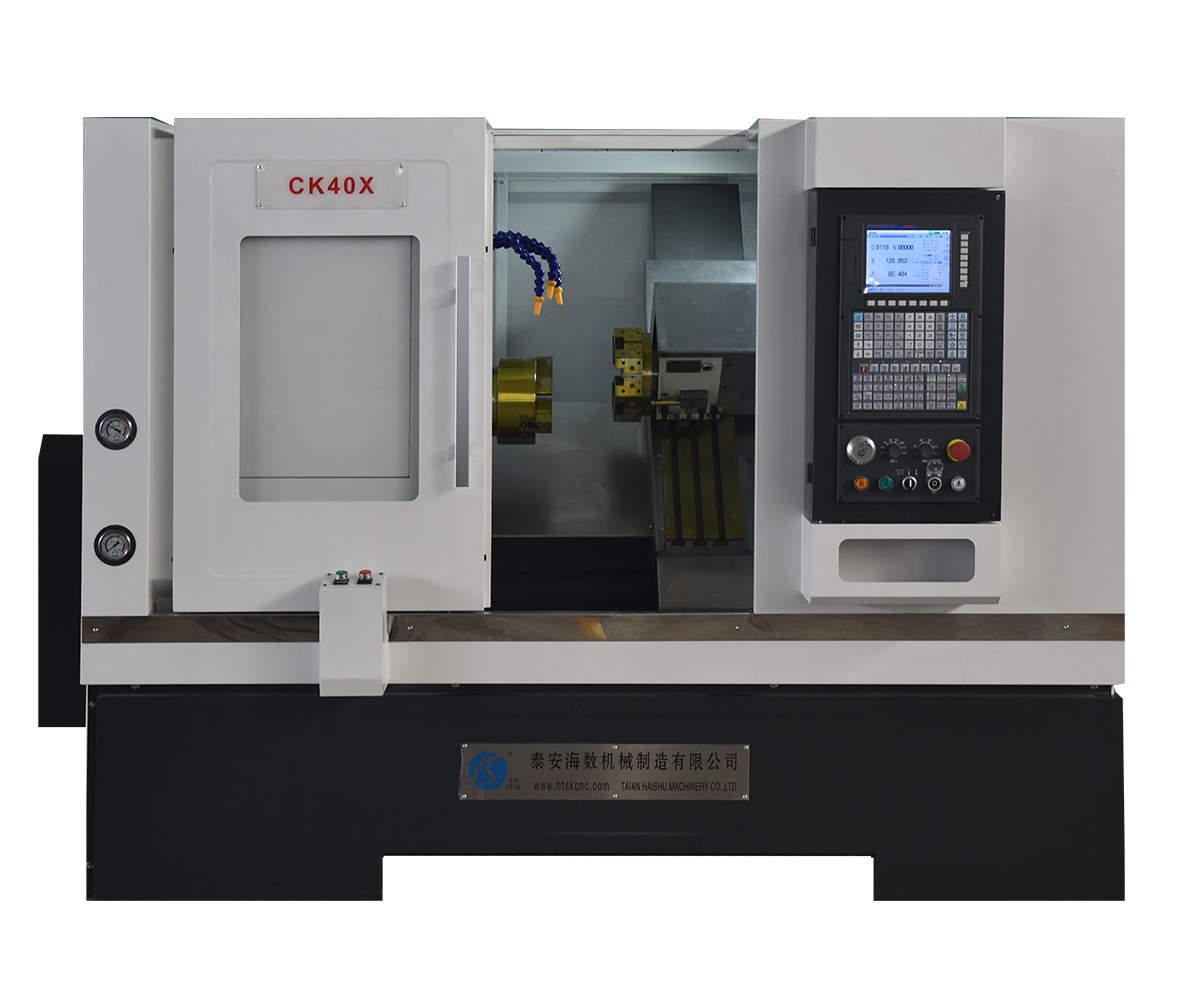




3. Key Components of CNC Lathes
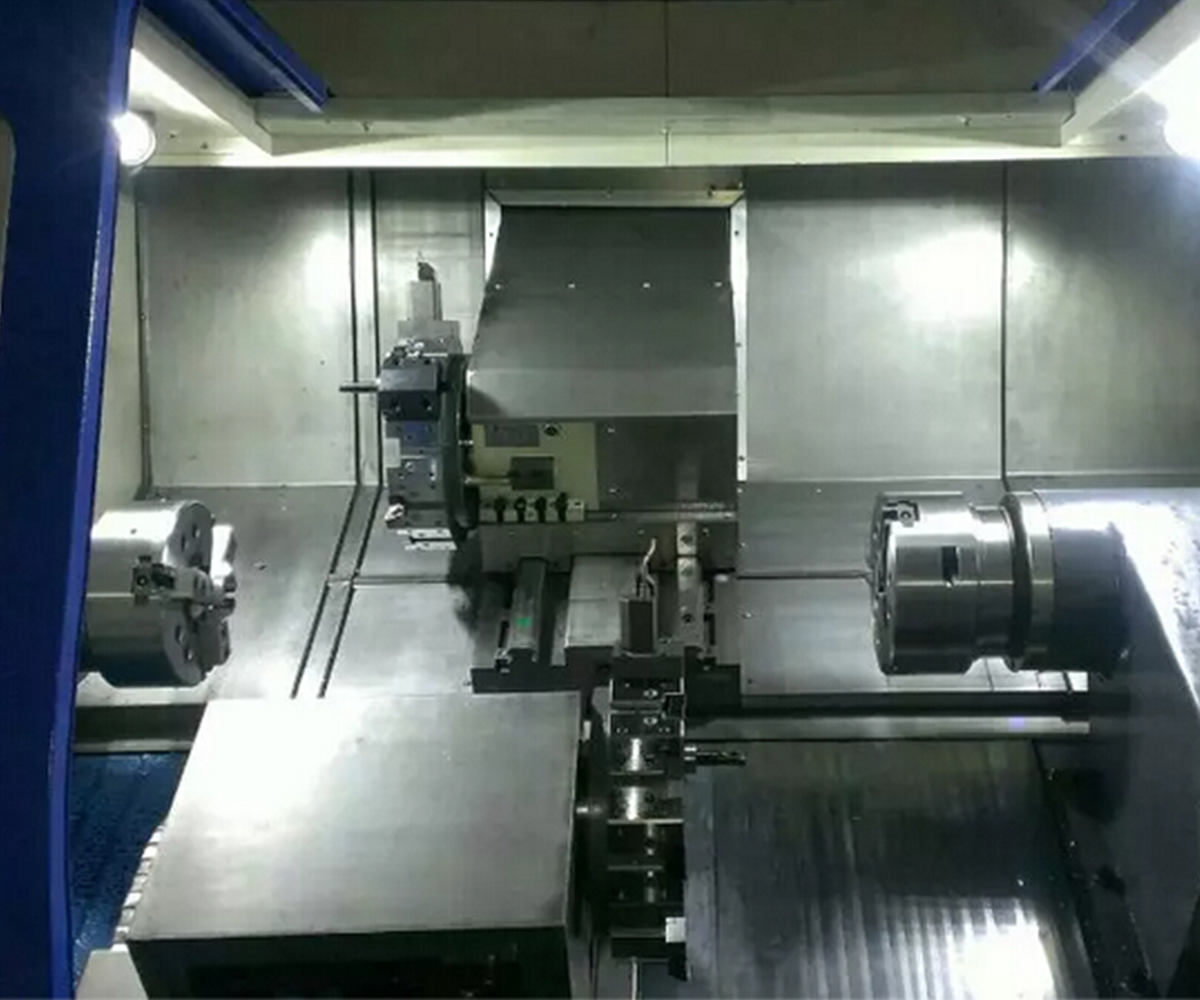
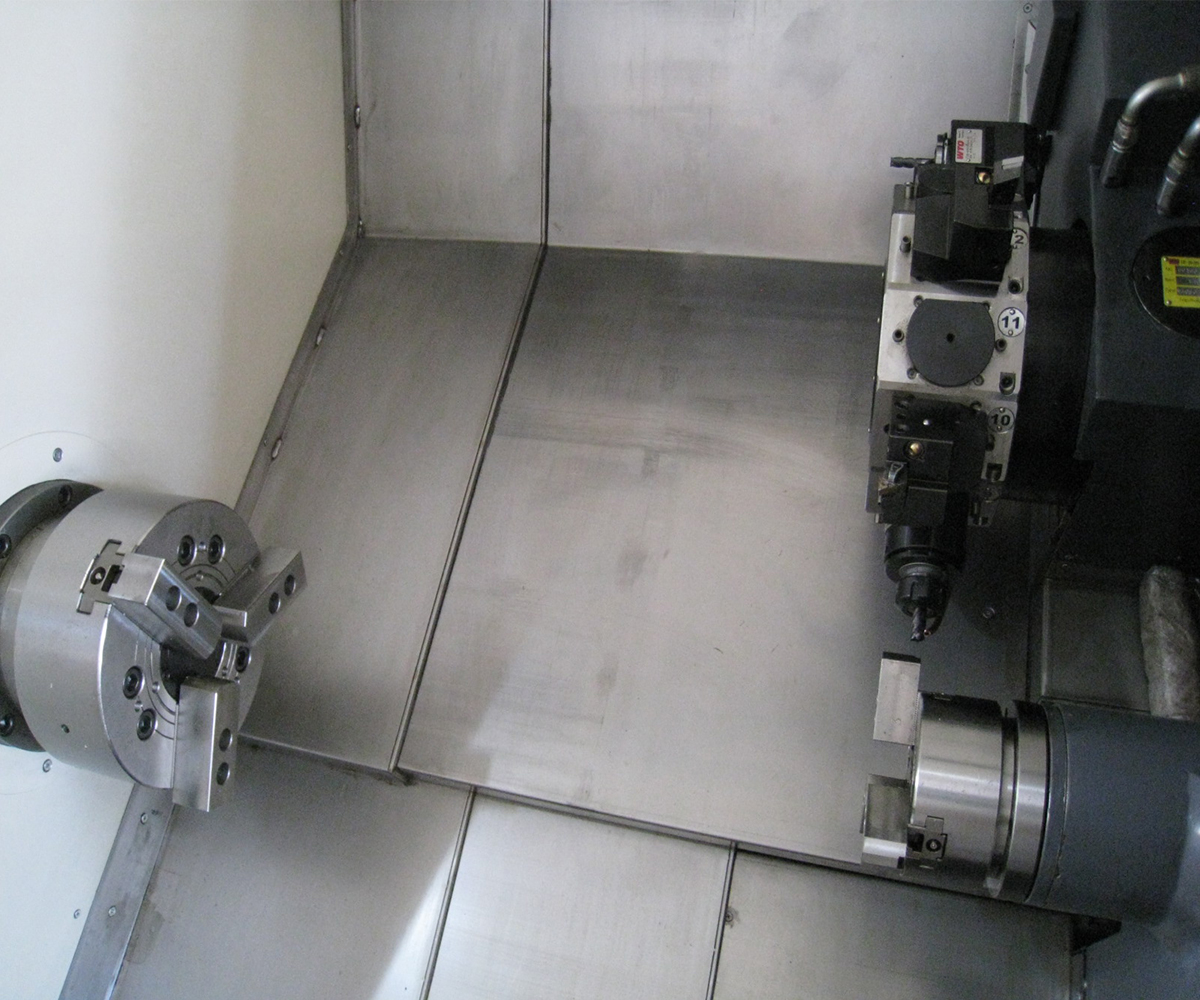
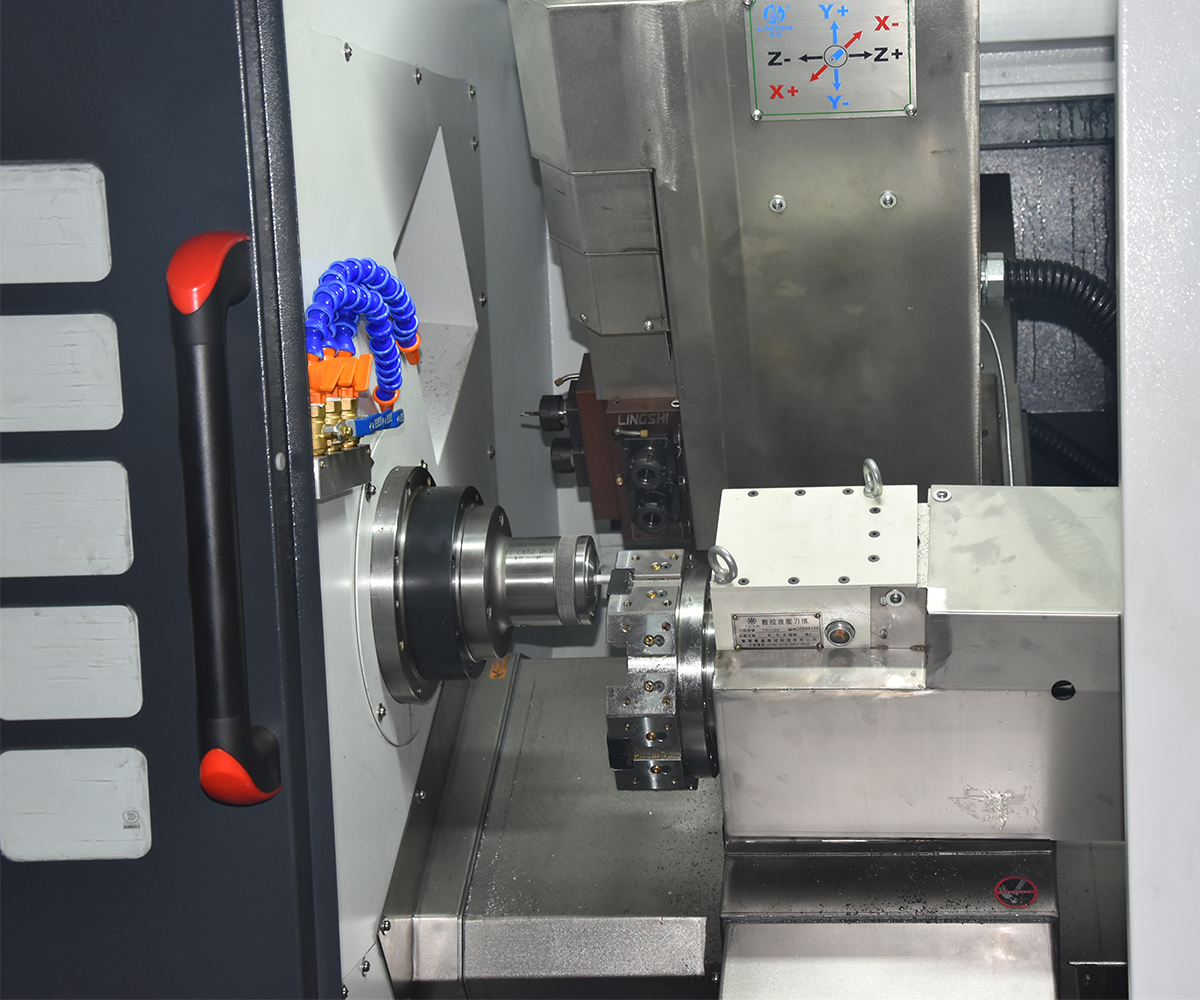
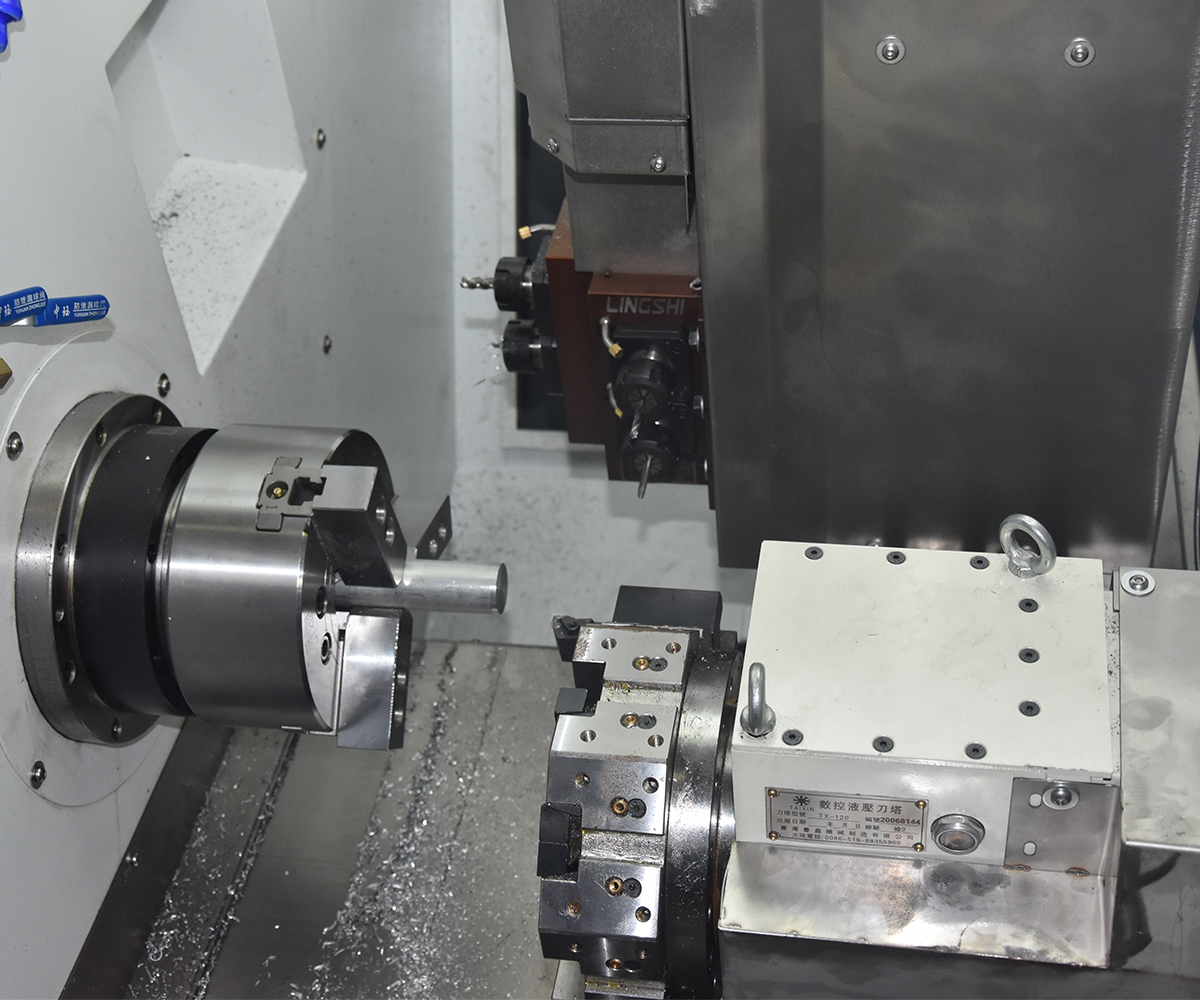
3.1 Spindle and Sub-Spindle
The spindle and sub-spindle are common rotating axes in CNC lathe used to drive cutting tools and enable various machining operations. The spindle serves as the primary rotational axis, driving the main cutting tool for cutting operations, and typically possesses high speed and power. The sub-spindle, on the other hand, is an additional rotational axis that can operate independently. It is used for auxiliary cutting operations or to accomplish complex machining tasks, typically with lower power and speed. The simultaneous machining capability of the spindle and sub-spindle is suitable for processing long bar materials, part transfer, and intricate machining. Their collaborative operation enhances machining efficiency, productivity, and quality.
3.2 Machine Bed and Guideways
The machine bed and guideways are essential components of CNC machine tools. The machine bed forms the foundation structure of the machine tool, providing support and stability for various components. It needs to possess sufficient rigidity and stability. The guideways form the motion system of the machine tool, enabling precise positioning and alignment of the cutting tool and workpiece. Guideways can come in various forms, such as flat guideways, V-shaped guideways, rolling guideways, and linear guideways. The selection of guideways depends on the machine tool type, machining requirements, and budget considerations. Well-designed machine beds and guideways provide a stable machining platform, high-precision motion control, and superior machining results. HAISHU’s CNC lathe beds are manufactured using high-quality cast iron material for increased rigidity. They incorporate a combination of hardened guideways and linear guideways to enhance machining efficiency and precision.
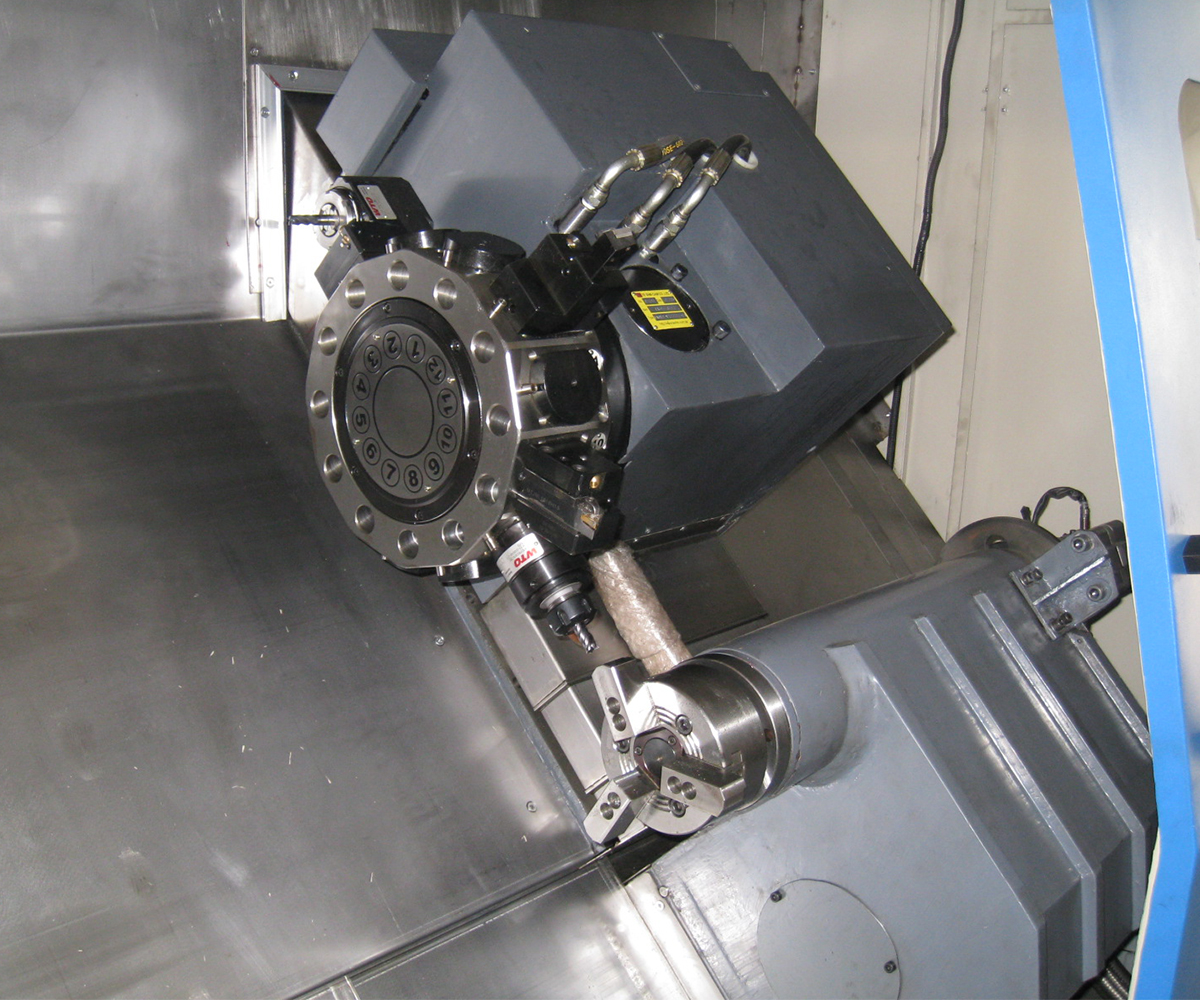
3.3 Turret and Cutting Tools
The turret is a critical component of CNC lathe used for installing and controlling cutting tools. It typically consists of a tool holder and tool post, which secure and adjust the position and angle of the cutting tools. The turret can accommodate multiple tool posts, enabling quick tool changes during the machining process.
Cutting tools are essential tools used on CNC lathe for cutting and material removal. Common cutting tools include turning tools, milling cutters, drills, and more. The selection of cutting tools depends on the material being machined and the required machining operations. Cutting tools come in various shapes, sizes, and cutting edges to meet different machining requirements.
The selection and adjustment of the turret and cutting tools are crucial for achieving high machining quality and efficiency. In CNC lathe, operators can specify the tool selection, position, and cutting parameters in the programming interface based on the machining requirements. Turret adjustments can be made through the controller or manual operations to ensure proper installation and adjustment of the cutting tools. HAISHU provides detailed production plans and tool recommendations to simplify CNC lathe operation and workpiece machining for our customers. We offer various turret options, such as electric and hydraulic turrets. Additionally, there are multiple tool station options, including four-station, six-station, eight-station, and twelve-station. Turrets are also available in different types, such as hydraulic turrets and power turrets, allowing customers to choose according to their specific needs.
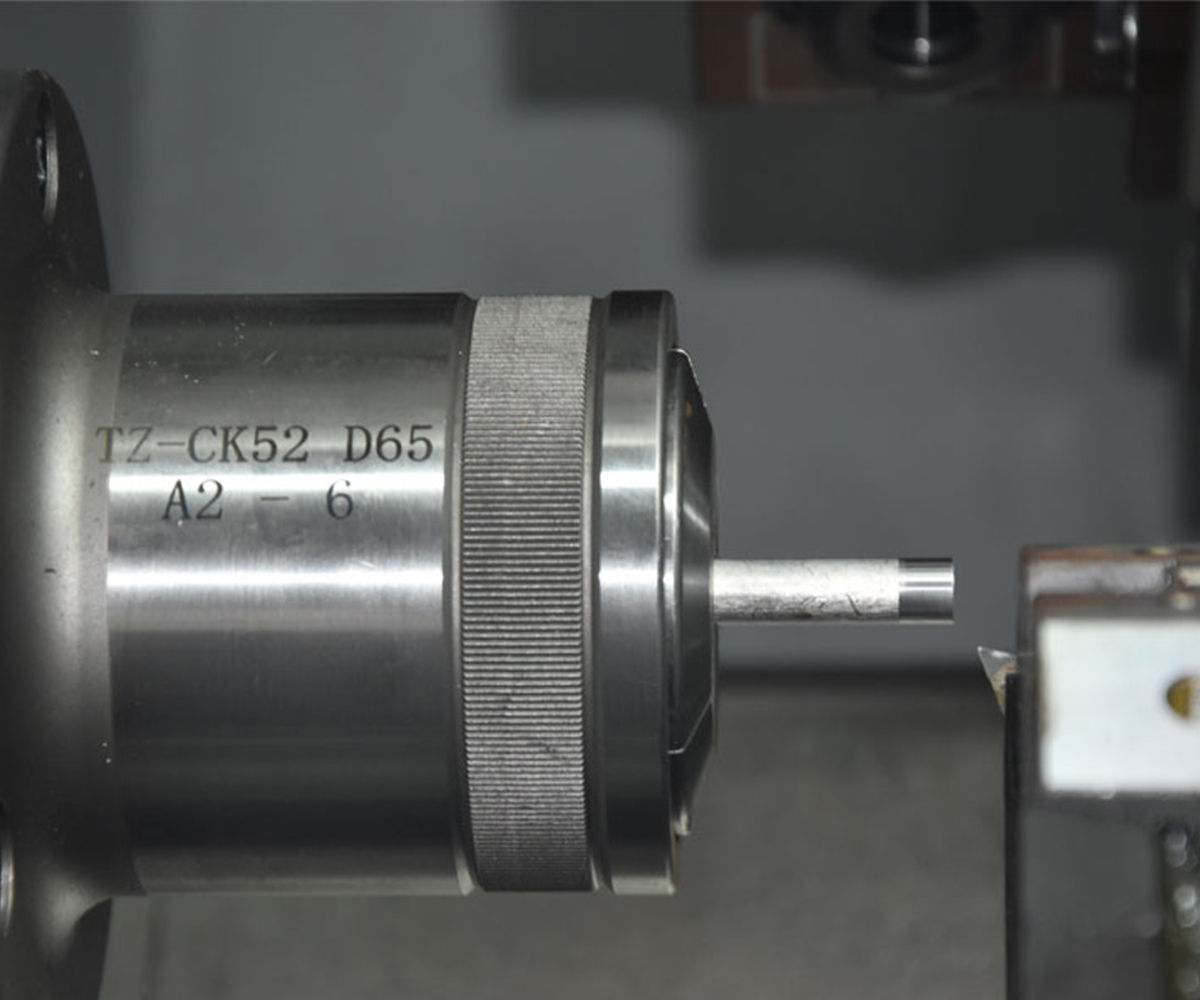
3.4 Chuck and Workholding Devices
A chuck is a device used for holding workpieces and typically consists of adjustable jaws. They can be adjusted according to the shape and size of the workpiece to ensure its stable position during the machining process.
Workholding devices are used to secure workpieces and can be mechanical fixtures, pneumatic fixtures, hydraulic fixtures, or vacuum fixtures, among others. They secure the workpiece in the desired position by generating clamping forces, ensuring that the workpiece does not move or deform during machining.
Chucks and work-holding devices play a crucial role in CNC lathe by providing stable gripping force and position control, ensuring the accuracy and quality requirements of workpiece machining. The HAISHU brand has gained customer recognition by offering a variety of choices and solutions in the field of fixtures, allowing customers to achieve optimal workpiece holding solutions.
3.5 CNC Controller and Program Storage
The CNC controller is the core component of a CNC lathe, responsible for receiving, interpreting, and executing machining program instructions, and controlling the machine’s motion and operations. It typically consists of an embedded computer or a dedicated CNC controller with high-speed computation and precise control capabilities.
Program storage is an essential part of the CNC control system, used to store and manage multiple machining programs and related data. It can take the form of internal memory, external storage devices, or cloud storage. Program storage allows operators to select and load appropriate machining programs as needed to meet the machining requirements of different workpieces.
By combining the CNC controller and program storage, operators can input machining commands through the programming interface and load the corresponding machining programs to achieve precise motion control and machining operations. Such a control system provides high flexibility and programmability, enabling CNC lathe to adapt to various complex machining needs and improve production efficiency and machining quality.
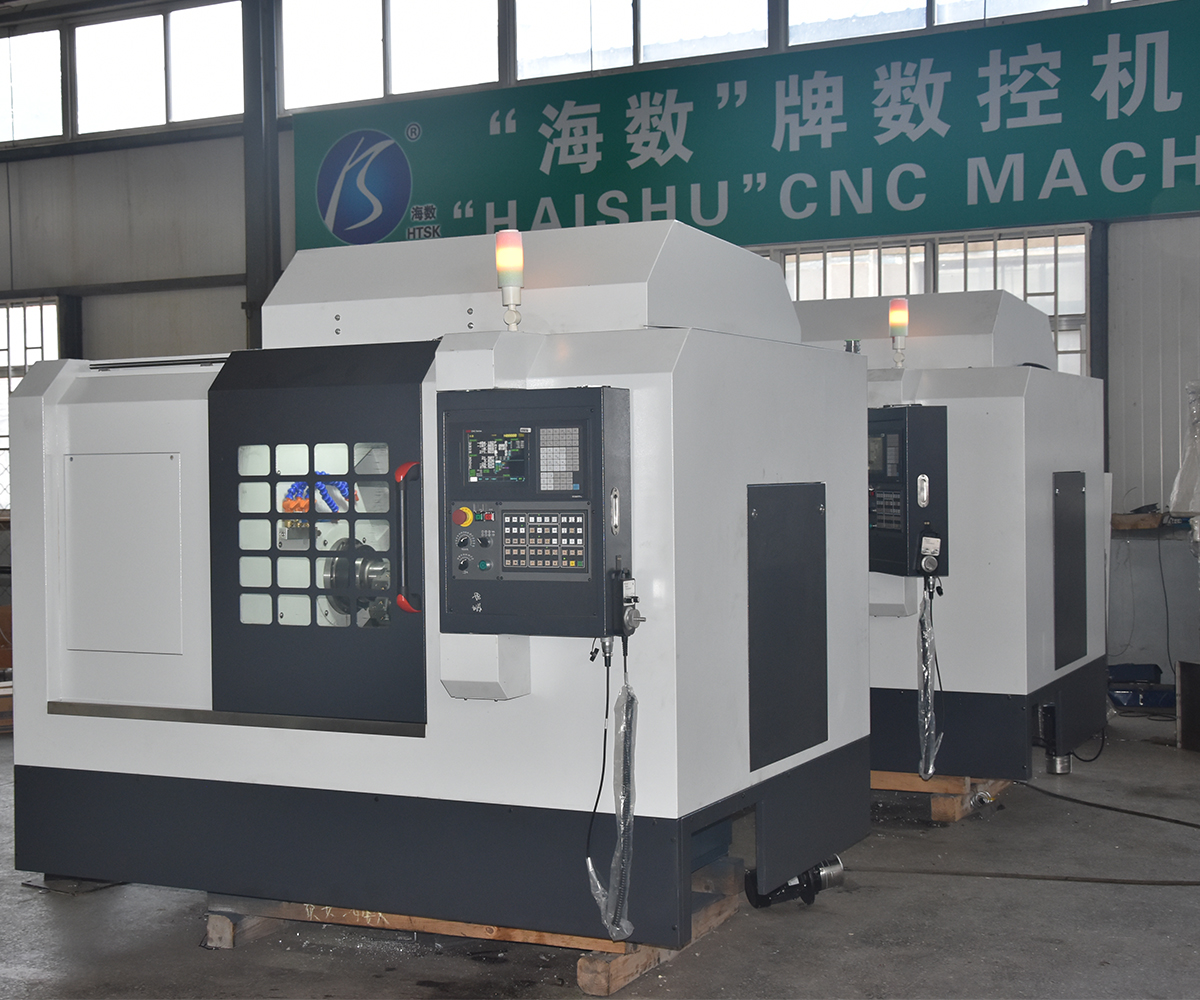
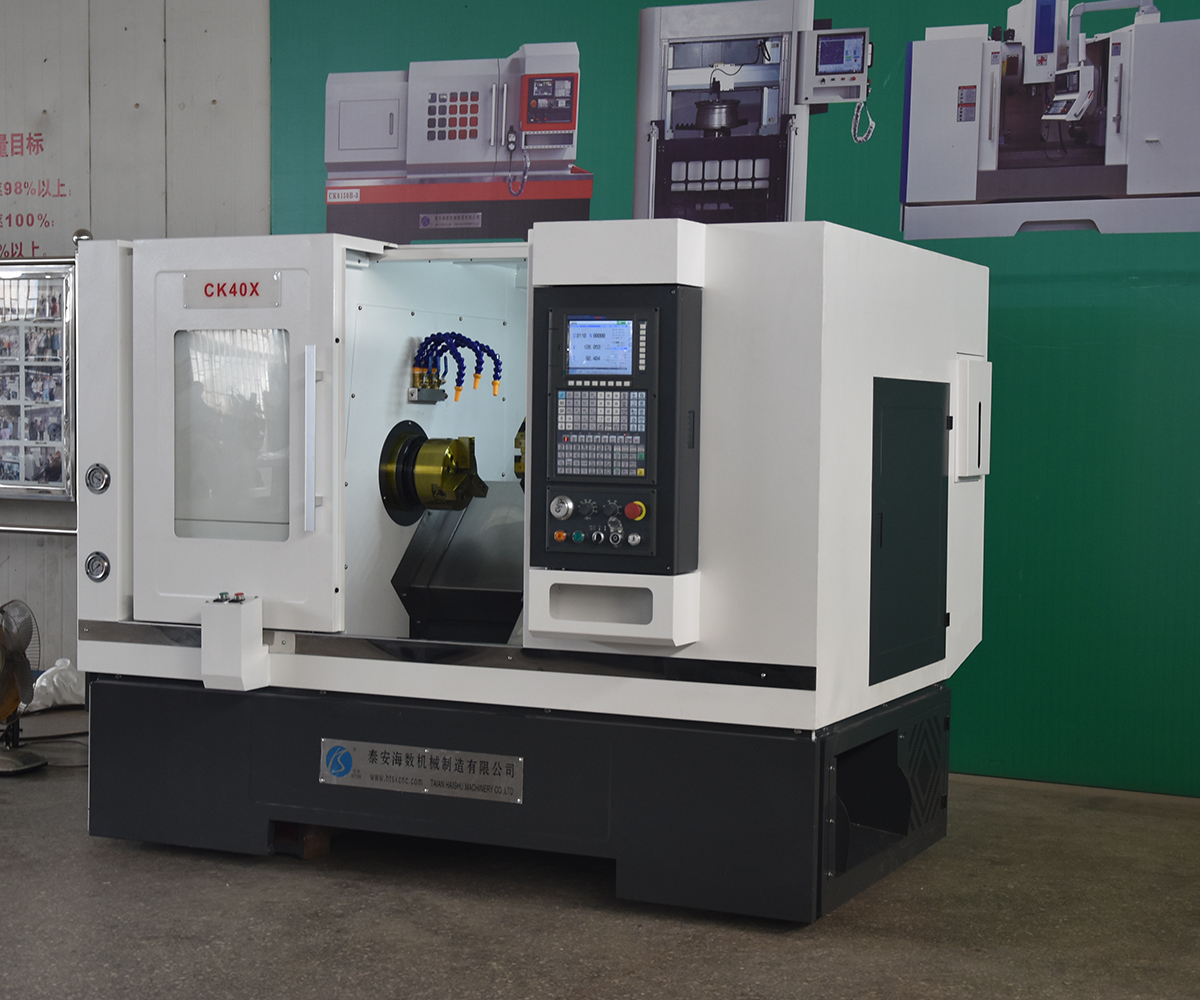
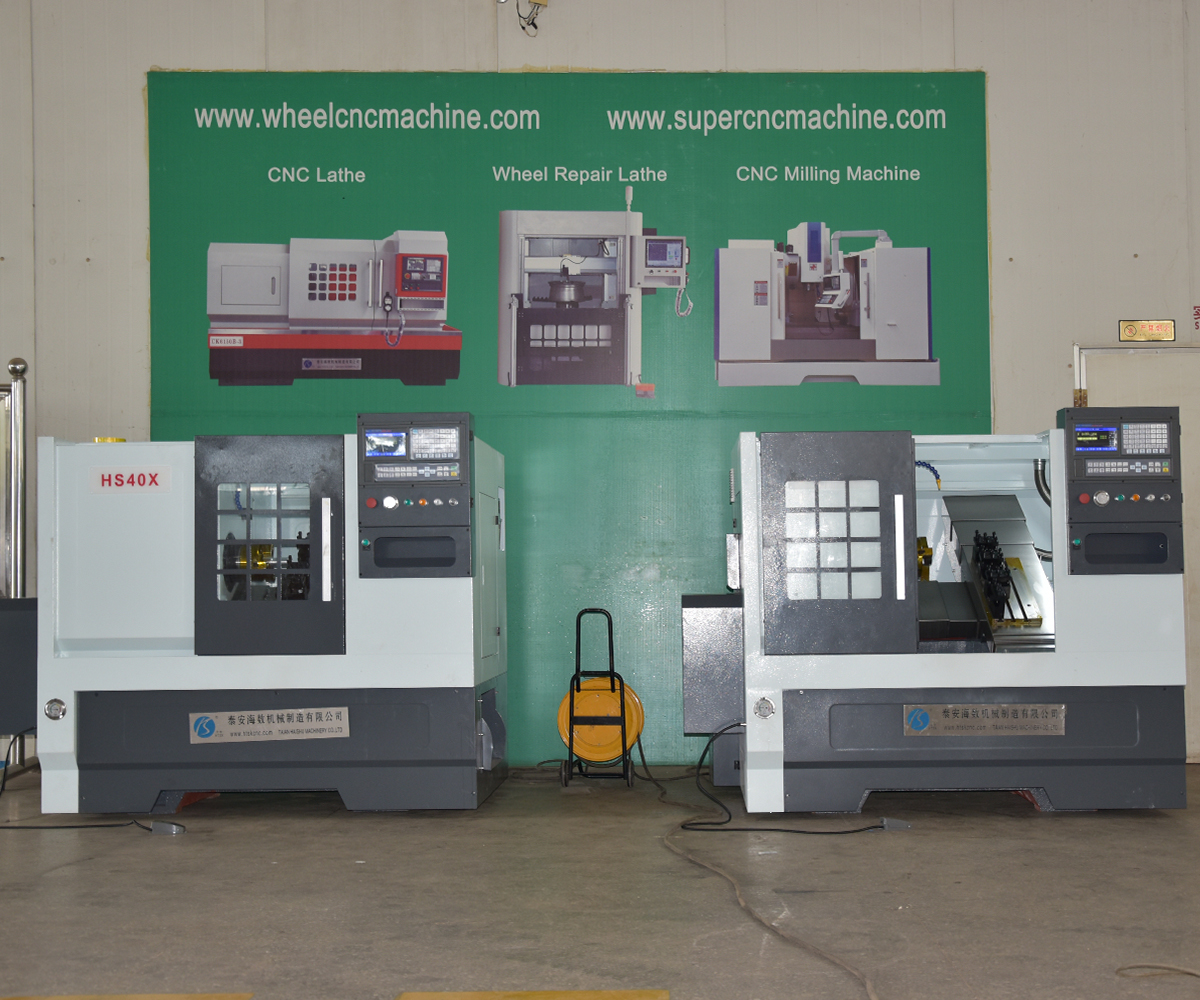




4. CNC lathe Applications
4.1 Manufacturing and Parts Machining
CNC lathe play a crucial role in manufacturing and parts machining. Through computer control, they can efficiently and accurately machine various components, improving production efficiency and machining quality.
4.2 Automotive Industry and Aerospace
CNC lathe have significant roles in the automotive industry and aerospace sector. In the automotive industry, CNC lathe are used to machine various automotive parts such as engine components, brake system elements, and chassis parts. They achieve high-precision cutting and shaping, ensuring the quality and accuracy requirements of the parts.
In the aerospace field, CNC lathe are used to manufacture critical components for aircraft and spacecraft. They can machine complex aerospace parts such as engine components, wing structures, and spacecraft casings. The high precision and stability of CNC lathe ensure the safety and performance requirements of aerospace vehicles.
4.3 Healthcare and Biotechnology
In the healthcare sector, CNC lathe are used to manufacture medical devices such as artificial joints, implants, and surgical tools. They achieve high-precision machining, ensuring the quality and accuracy requirements of medical equipment, and providing safer and more reliable medical treatments.
In the biotechnology field, CNC lathe are used to manufacture biotechnology products such as laboratory instruments, biochips, and gene sequencing equipment. They can machine small-sized components and microstructures, achieving precise machining and assembly, and meeting the requirements of biotechnology research and applications.
4.4 CNC lathe Applications in Other Industries
In shipbuilding, CNC lathe are used to machine ship structures, propulsion systems, and ship components, ensuring high precision and stability of ships.
In the energy sector, CNC lathe are used to manufacture components for nuclear power plants, wind turbine generators, and oil drilling rigs, meeting the machining needs of energy equipment.
In the electronics industry, CNC lathe are used to machine electronic device enclosures, connectors, and conductive components, ensuring the precision and quality of electronic products.
In construction machinery manufacturing, CNC lathe are used to machine excavator components, loader structures, and road roller parts, providing efficient engineering machinery solutions.
In furniture manufacturing, CNC lathe are used to machine furniture parts and decorations, achieving personalized customization and fine machining.
HAISHU company can provide you with tailored CNC machines for your CNC lathe needs in every industry. This is why we have provided such detailed information about CNC lathe.
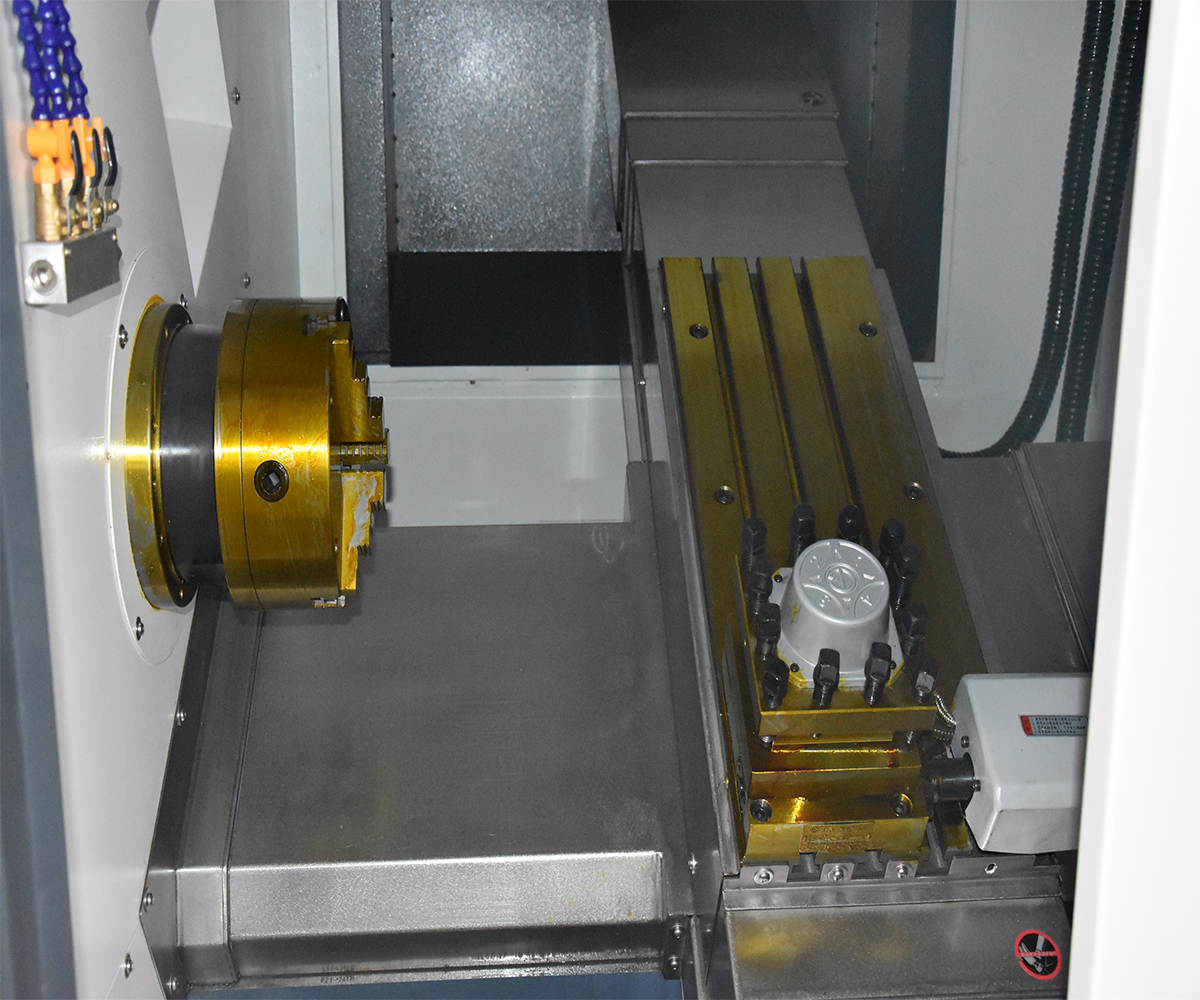



5. Advantages and Challenges of CNC Lathes
5.1 Advantages of Accuracy and Reproducibility
Firstly, CNC lathe achieve precise control of tool movement and machining processes through computer control systems. They can achieve high-precision cutting and shaping, ensuring the dimensional and geometric accuracy requirements of machined parts. Compared to traditional manual operations or conventional mechanical lathes, CNC lathe can more accurately control the machining process, reducing the impact of human errors.
Secondly, CNC lathe have excellent repeatability. Once a program is written and loaded into the CNC lathe, it can repeatedly execute the same machining program, ensuring the consistency of dimensions and shapes for each part. This makes batch production and series production more feasible and efficient, reducing the variability and errors caused by manual operations.
5.2 Advantages of Production Efficiency and Quick Delivery
CNC lathe have the advantage of improving production efficiency and achieving quick delivery. The automated machining process and flexible programming capability enable them to quickly complete tasks and adapt to different machining requirements. This improves production efficiency, accelerates the manufacturing process, and enables businesses to respond quickly to market demands, achieving quick delivery.
5.3 Challenges of Skill Requirements and Training
Operating CNC lathe requires familiarity with CNC programming and the operating interface, an understanding of the tool path and setting of machining parameters, as well as some knowledge of monitoring and troubleshooting during the machining process. Operators need to acquire these skills to ensure proper machining and high-quality part production.
However, training for CNC lathe operations also faces some challenges. Firstly, CNC lathe require high technical and operational requirements, requiring a significant amount of training and practical experience to master proficiently. Secondly, due to the continuous updates and evolution of CNC lathe technology, operators need to continuously learn new techniques and functionalities to stay in sync with the industry.
Additionally, CNC lathe operation also requires a thorough understanding of safety precautions and operating procedures to ensure the safety of operators and the normal operation of the equipment. To facilitate better utilization of CNC lathe, HAISHU company provides detailed instructional videos and on-site services to help users overcome challenges in using CNC lathe.
5.4 Considerations of Equipment Investment and Maintenance Costs
Firstly, the purchase cost of CNC lathe is relatively high. This is due to advanced technologies such as high precision, automation, complex control systems, and mechanical structures. Users need to consider their budget and production requirements to assess whether they can afford this investment.
Secondly, maintenance and upkeep of CNC lathe also incur costs. This includes regular maintenance, replacement of parts, repairs, and software updates. Users need to allocate funds for maintenance and ensure the proper operation and long-term reliability of the equipment.
Additionally, the energy consumption of CNC lathe needs to be considered. CNC lathe typically require electricity, hydraulic power, or pneumatic power, and users need to evaluate their energy costs and consider the energy efficiency of the equipment.
Lastly, training operators also incurs costs. To ensure the proper operation and safety of CNC lathe, operators need to undergo training and education to understand the operating procedures and safety precautions of the equipment.
To provide better service to customers, HAISHU company also offers replacement parts for vulnerable components and provides a one-year warranty service, reducing the user’s operating costs. All of this is aimed at allowing users to enjoy the perfect service of HAISHU CNC lathe.




6. Conclusion
CNC lathes are high-precision and automated machining equipment with a wide range of applications. They achieve precise control of tool movement and machining processes through computer control systems, providing high-precision and highly repeatable machining solutions. CNC lathes have the advantages of improving production efficiency and achieving quick delivery, enabling fast completion of tasks, adapting to different machining requirements, and responding quickly to market demands. However, operating CNC lathes requires specific skills and training, and equipment investment and maintenance costs need to be considered. Overall, CNC lathes are indispensable tools in modern manufacturing, driving the development and progress of various industries. As a CNC lathe manufacturer with over 20 years of experience, HAISHU Company has abundant solutions to tailor CNC lathes to customers’ needs, even providing OEM production services for distributors. We have a strong presence and sales experience in more than 80 countries and regions worldwide. We recommend and provide the most cost-effective CNC lathes based on customers’ drawings, materials, and configurations.




